Two models are built with a ML technique. Decision tree technique is used in
order to predict the “CPI” values whereas random forest technique is used to
predict the “temperature” values.
Decision Tree
Decision Tree
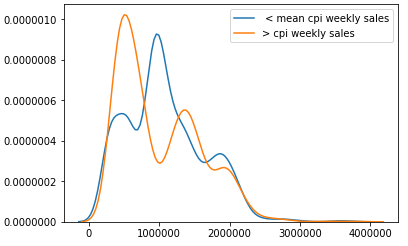
In our Decision Tree ML model we focused predicting whether or not CPI values
in each date were under the mean or above it. In order to build this model we first
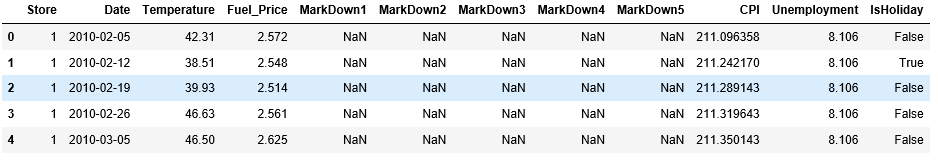
got rid of the features that were not useful to predict CPI values like Date, Year,
IsHoliday and Markdowns. Than in order to map the CPI values we renamed the
current CPI column that contained the values to ‘cop’,took the mean of all the
values in this column and then created another column named ‘cpi_mod’ which
stores binary values allocated by whether or not the CPI value of the corresponding
line was below or above the mean (1 for above, 0 for below)
cop_mean = walmart_features[“CPI”].mean()
walmart_features[“cpi_mod”] = 0
walmart_features.loc[walmart_features[“CPI”] >= cop_mean, “cpi_mod”] = 1
The attribute we wanted to predict and other features are used to create a dataset
with 70% of the original dataset as train and 30% as a test data set to evaluate the
Decision Tree
y = walmart_features[‘cpi_mod’] # this is what we want to predict.
X = walmart_features.drop(‘CPI’,axis =1)
X = X.drop(‘cpi_mod’,axis = 1) # these are our features
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42, test_size=0.30)
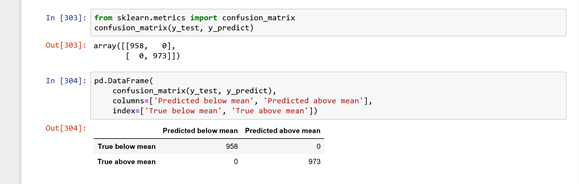
The above image shows the accuracy score of our Decision Tree and it can be seen
that it has resulted with the perfect score of 1 which means that the model
predicted each CPI value correctly. The results can be evaluated more clearly with
the confusion matrix as seen below.
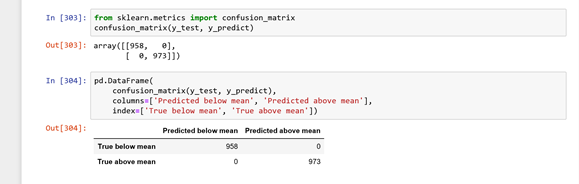
It is sensible that the model’s predictions aligns perfectly with the real data since its accuracy was 100% which means that our model only predicted the CPI below mean where it was originally below mean and as above mean where it was originally above mean.